(i) Scalability and Efficiency Limitation
시뮬레이션에 포함된 에이전트의 scale는 특정 시뮬레이션을 수행할 때 중요할 수 있다. 작은 scale의 시뮬레이션은 현실 세계의 복잡성을 정확하게 나타내지 못해 시뮬레이션의 신뢰성과 현실성이 떨어질 위험이 있다
에이전트의 규모를 늘리면 시뮬레이션 플랫폼의 확장성과 효율성에 대한 challenge가 발생
구체적으로, 에이전트가 작업과 통신을( execute their tasks and communications )적절한 순서로 효율적으로 조직하는 것은 실행 시간을 줄이고 정확한 결과를 보장하는 데 어려움이 있다. 또한, 시뮬레이션 플랫폼은 대규모 에이전트 기반 시뮬레이션에서 에이전트 간 및 에이전트-환경 상호작용을 지원하기 위해 high-frequency access 을 처리할 수 있어야 합니다.
(ii)Unsatisfied Population Distributions and Agent Diversity
대규모 시뮬레이션에서 에이전트들이 특정 population distribution 를 따르면서 다양한 행동을 보이는 것이 필수적입니다 https://arxiv.org/abs/2402.17505 에이전트들에게 간단한 배경만을 부여하면, 많은 수의 동질적인( homogenized )에이전트가 발생하게 되어 의미 있는 통찰력을 도출하기 어려워집니다. 또한, 기존 연구들은 연령, 교육, 직업 등 다양한 관점에서 에이전트의 인구 분포를 지정하는 방법을 거의 고려하지 않아 시뮬레이션의 현실성을 감소시킵니다.
BASES: Large-scale Web Search User Simulation with Large Language Model based Agents
Due to the excellent capacities of large language models (LLMs), it becomes feasible to develop LLM-based agents for reliable user simulation. Considering the scarcity and limit (e.g., privacy issues) of real user data, in this paper, we conduct large-scal
arxiv.org
(iii)Difficult Management Processes
에이전트의 규모가 증가함에 따라, 많은 수의 에이전트를 여러 devices에 분산시켜 초기화, 실행, 종료( initialization, execution, and termination )를 포함한 시뮬레이션을 관리하는 것은 상당한 노력이 필요 https://arxiv.org/abs/2402.16333
Unveiling the Truth and Facilitating Change: Towards Agent-based Large-scale Social Movement Simulation
Social media has emerged as a cornerstone of social movements, wielding significant influence in driving societal change. Simulating the response of the public and forecasting the potential impact has become increasingly important. However, existing method
arxiv.org
상태, 행동, 상호작용을 모니터링하는 데 어려움이 있어, 그룹 수준 및 개인 수준의 유용한 행동을 신속하게 식별하기 어렵다. 이는 시뮬레이션을 최적화하고 연구를 발전시키기 위한 중요한 insight을 발견하는 데 장애(hinder)가 될 수 있다. 따라서 대규모 에이전트를 관리하기 위한 사용하기 쉬운 도구가 에이전트 기반 시뮬레이션 플랫폼에서 제공되어야 한다.
related work
Agent-Based Simulation Frameworks
https://arxiv.org/abs/2405.06700
LLM-Augmented Agent-Based Modelling for Social Simulations: Challenges and Opportunities
As large language models (LLMs) continue to make significant strides, their better integration into agent-based simulations offers a transformational potential for understanding complex social systems. However, such integration is not trivial and poses num
arxiv.org
https://arxiv.org/abs/2403.06144
Simulating Family Conversations using LLMs: Demonstration of Parenting Styles
This study presents a framework for conducting psychological and linguistic research through simulated conversations using large language models (LLMs). The proposed methodology offers significant advantages, particularly for simulating human interactions
arxiv.org
https://arxiv.org/abs/2404.10179
Scaling Instructable Agents Across Many Simulated Worlds
Building embodied AI systems that can follow arbitrary language instructions in any 3D environment is a key challenge for creating general AI. Accomplishing this goal requires learning to ground language in perception and embodied actions, in order to acco
arxiv.org
education
https://arxiv.org/abs/2404.06711
MathVC: An LLM-Simulated Multi-Character Virtual Classroom for Mathematics Education
Mathematical modeling (MM) is considered a fundamental skill for students in STEM disciplines. Practicing the MM skill is often the most effective when students can engage in group discussion and collaborative problem-solving. However, due to unevenly dist
arxiv.org
societal
generative agents
BASES
Simulating family conversations using llms:
transportation
https://arxiv.org/abs/2309.13193
SurrealDriver: Designing LLM-powered Generative Driver Agent Framework based on Human Drivers' Driving-thinking Data
Leveraging advanced reasoning capabilities and extensive world knowledge of large language models (LLMs) to construct generative agents for solving complex real-world problems is a major trend. However, LLMs inherently lack embodiment as humans, resulting
arxiv.org
simulation
https://arxiv.org/abs/2404.16045
Elicitron: An LLM Agent-Based Simulation Framework for Design Requirements Elicitation
Requirements elicitation, a critical, yet time-consuming and challenging step in product development, often fails to capture the full spectrum of user needs. This may lead to products that fall short of expectations. This paper introduces a novel framework
arxiv.org
캐리커쳐
Compost: Characterizing and evaluating caricature in LLM simulations.
3.1 Actor-based Distributed Mechanism
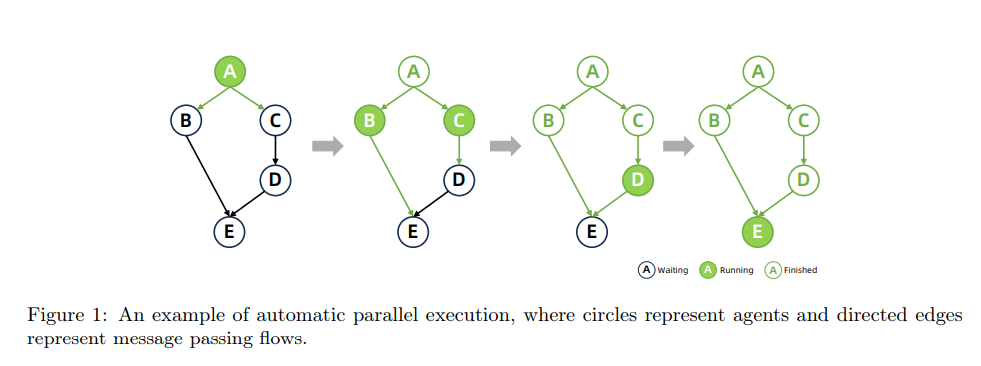
자동 병렬 실행, centralized workflow orchestration가 특징인 메커니즘
Automatic Parallel Execution
Centralized Workflow Orchestration
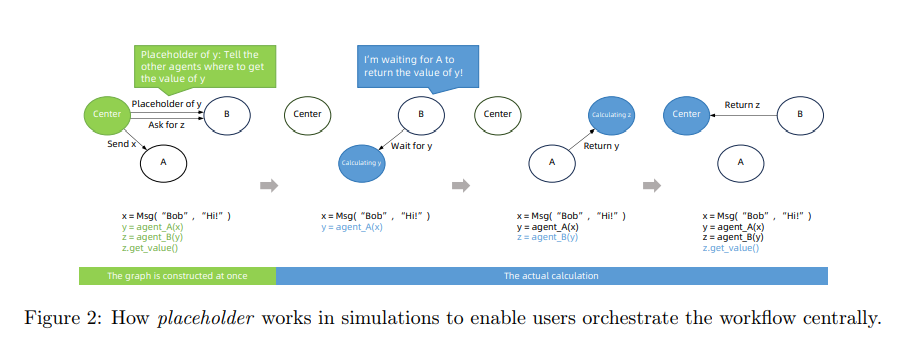
3.2 Agent-Environment Interactions
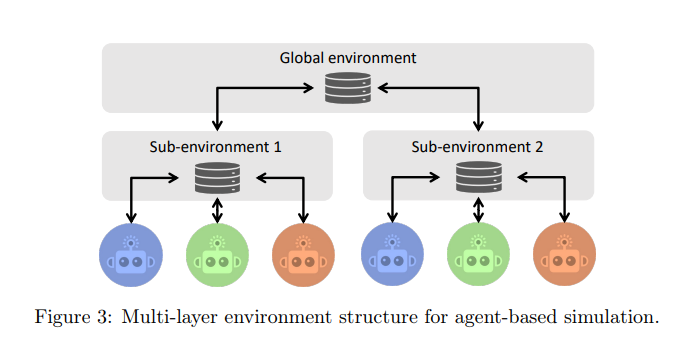
3.4 Management for Large-scale Agents
